The LLMNR protocol is usually enabled on all Windows systems and it’s the successor to NetBIOS. Both protocols are susceptible to spoofing and MITM attacks.
Follow the steps below to disable LLMNR via Group Policy(GPO):
- Open the Group Policy Management Console(gpmc.msc)
- Create a new GPO and link it to the OU containing the computer objects for which you want LLMNR disabled
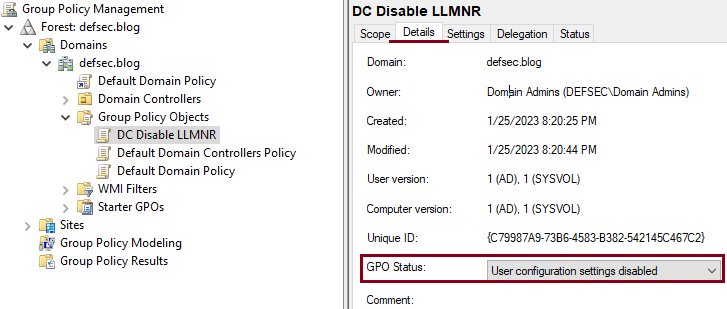
- Select the newly created GPO, click on the Details tab and disable the User Configuration settings for this GPO(in this particular case it’s best to disable the User Configuration settings entirely since we won’t need them. This reduces GPO processing times)
- Right click on the GPO and select Edit
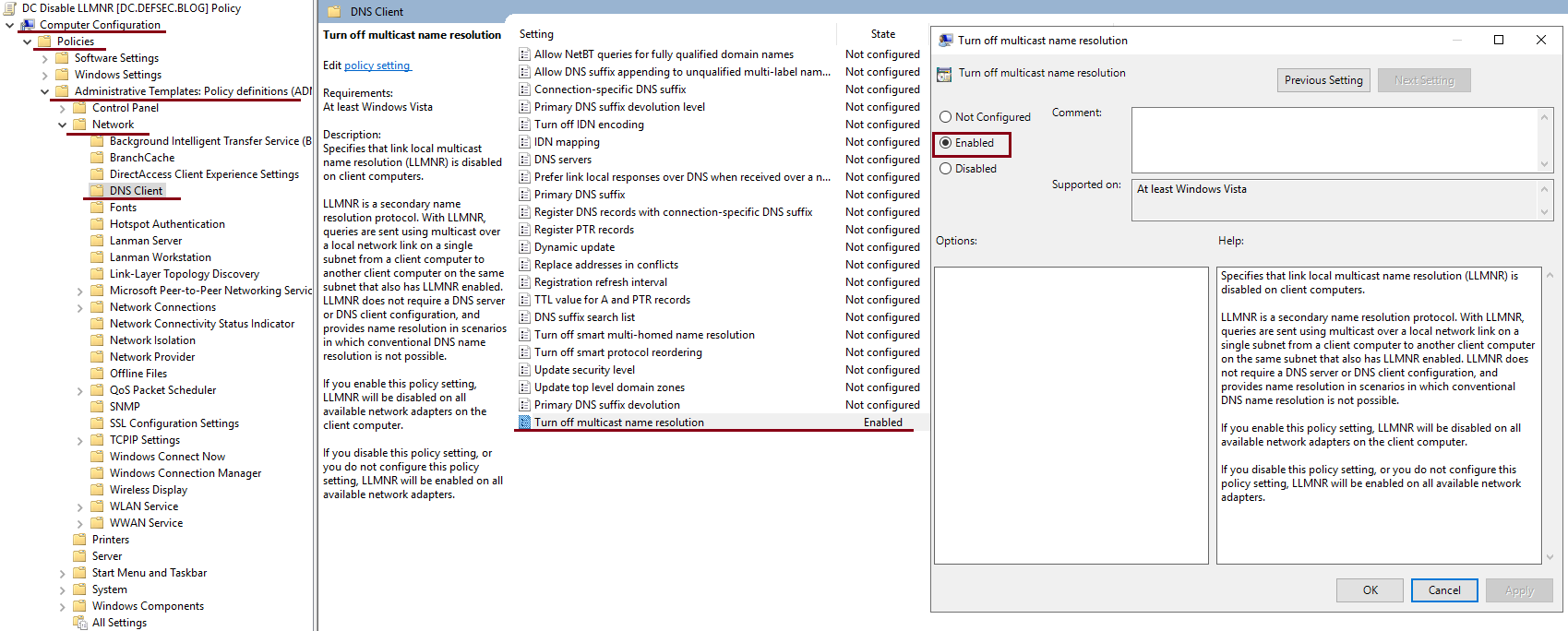
- Navigate to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Network -> DNS Client
- Open the “Turn off multicast name resolution” setting -> Select “Enable” and click OK
Follow the steps below to disable mDNS via GPO by using the predefined firewall rules(Inbound and Outbound) to blocks this service:
- Follow the above instructions to create a new GPO and link it to the appropriate OU or use the LLMNR GPO that you created in the previous step. Some people prefer to have a separate GPO for every single change and some are combining multiple settings in a single GPO. Personally, I use a mixture of both approaches. For the sake of simplicity, let’s use the same LLMNR GPO
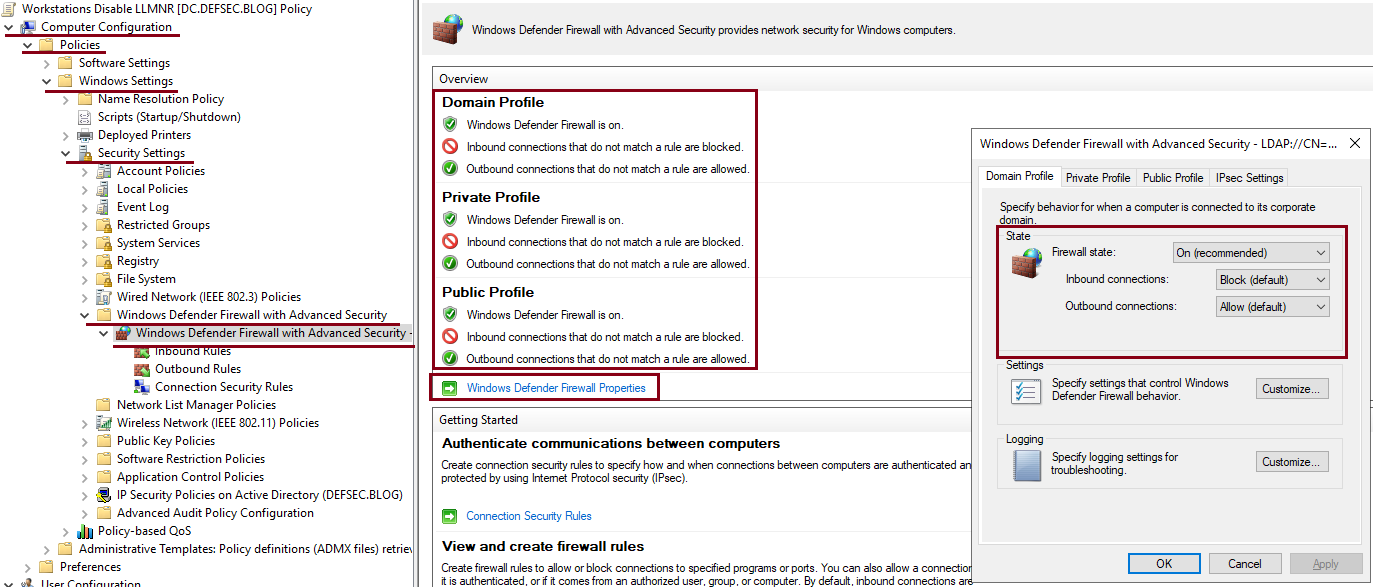
- Navigate to Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Windows Settings -> Security Settings -> Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security -> Windows Defender Firewall with Advanced Security
- Click on Windows Defender Firewall Properties and enable the firewall with default settings fro all profiles. There is more to the firewall settings(logs, notifications etc.) but this is not going to get covered here as it deserves its own post
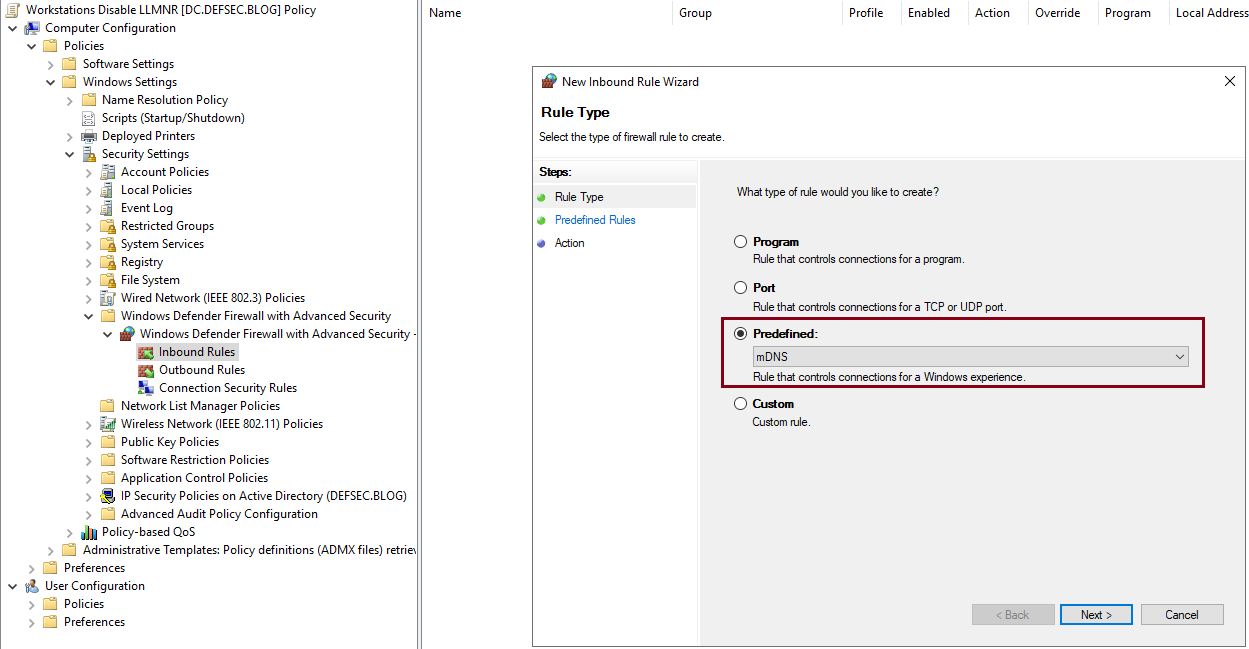
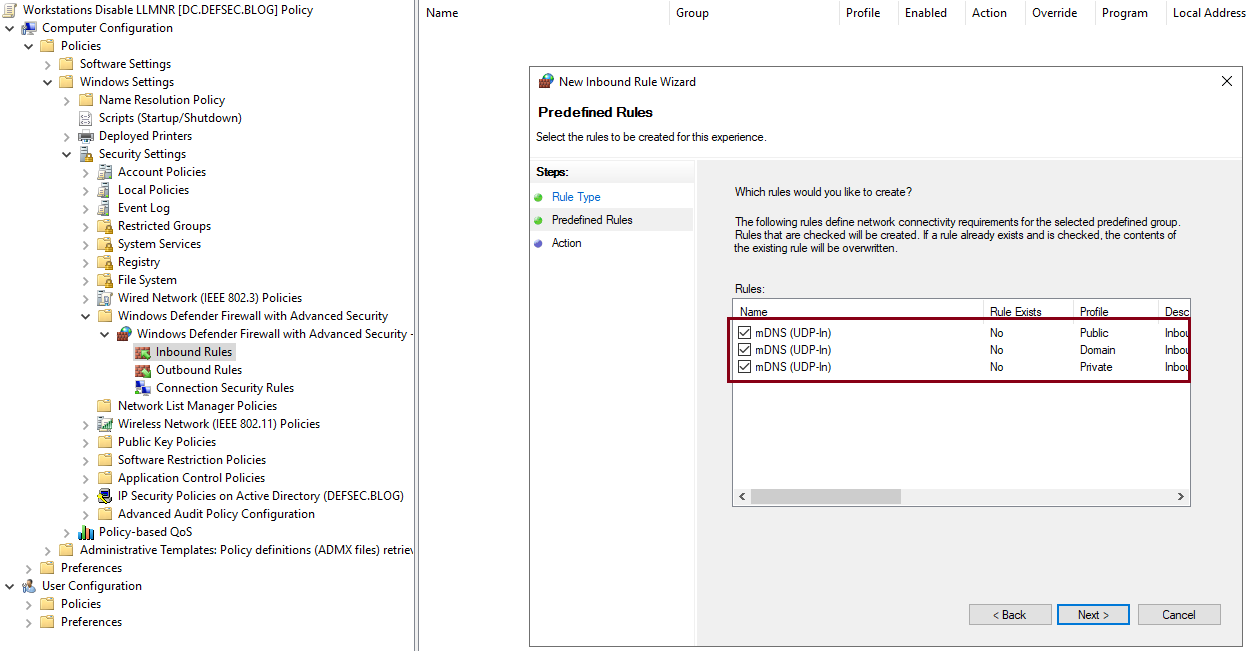
- Select the Inbound Rules -> Right click -> New Rule -> Select Predefined and pick mDNS from the drop down menu
- Click Next -> Select all three mDNS rules
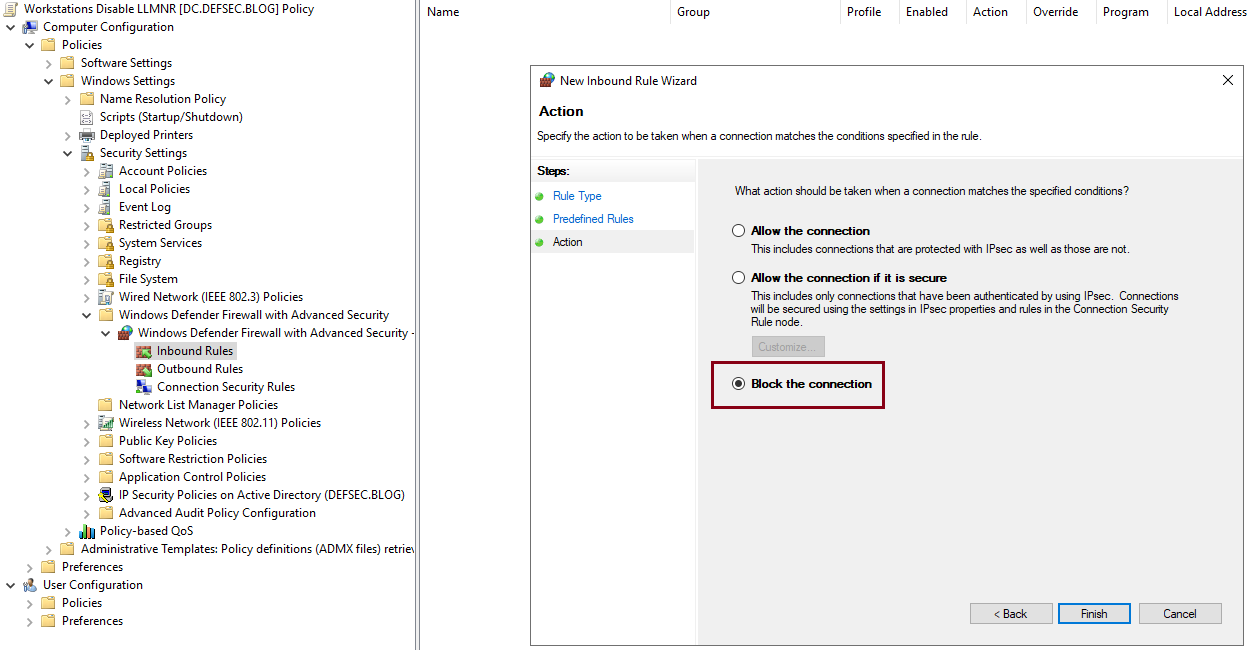
- Click Next and select Block the connection and click on Finish
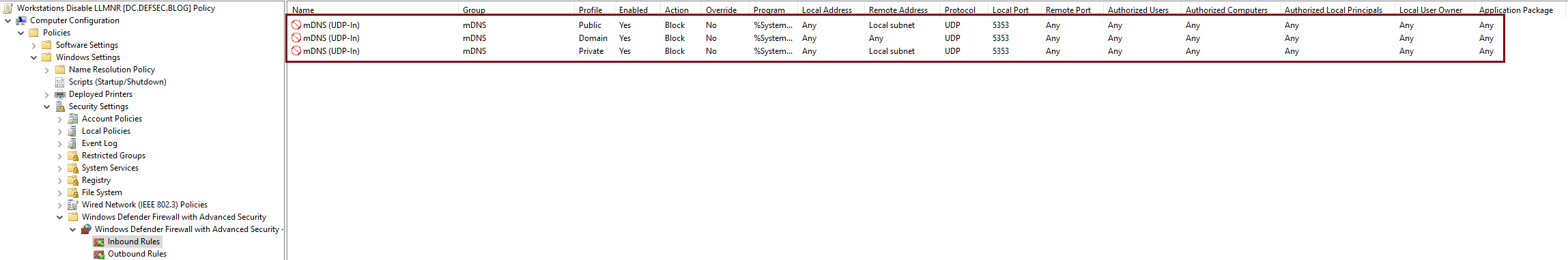
- You should see something similar to this
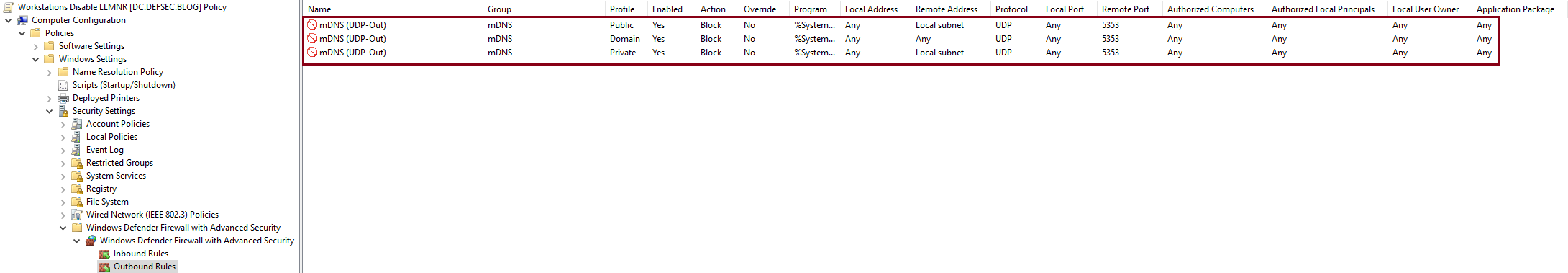
- Repeat steps #4 to #6 for the Outbound Rules
Note: The effectiveness of the above settings has been verified with Responder(on Kali Linux). For some reason implementing just the LLMNR portion didn’t actually disabled LLMNR and clients were still using it. They stopped only after disabling mDNS.